Top 3 Design System Structures
Many teams envision creating a design system as a difficult, time-consuming project. It forces team members to audit their user interface, create a repository of design system elements and design guidelines and combine it in a way it’s usable for the entire organization
It’s not the only way you structure a design system, though. There are some simpler methods of creating this toolkit that is meant to speed up the design process. Let’s explore the best approaches for arranging a design system structure that achieves these goals.
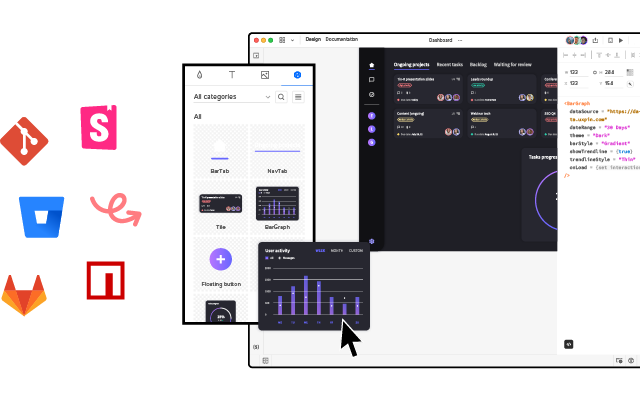
Maximize the use of your design system in prototyping. Bring your design system’s building blocks to UXPin and design interactive prototypes that your devs can quickly translate to code. Discover UXPin Merge.
What is a Design System Structure?
A design system structure is a comprehensive framework that helps manage design at scale by providing a set of shared principles, patterns, and tools. It enables a consistent, coherent, and efficient design process across multiple teams and projects. The structure typically includes various components, each serving a distinct role in the overall system.
By having a well-structured design system, organizations can ensure a cohesive user experience across all products and platforms, streamline the design and development process, and foster collaboration among team members.
Design systems can be broadly categorized into three types based on their scope, usage, and complexity. Here they are:
- Simple visual design repository
- Atomic design system structure
- Code-based design system structure.
Let’s explore them closely.
How Can You Structure a Design System?
When you combine design elements with the relevant documentation and guidelines, the system should form a coherent repository of things that are important for building user interfaces for a brand. But to achieve optimal design efficiency and system effectiveness, first, you must arrange it into a discernible structure. One that best suits your team’s needs and your organizational design objectives.
Simple visual design repository
This is the most basic of design system structures. As the NN Group explains, these visual design repositories come in various configurations, though the core focus here is simplicity.
At its fundamental level, a simple repository’s primary design system components consist of a style guide, a component library, and a pattern library. Together, these form the essentials for any functioning design system repository.

This structure only contains the essentials that constitute the system. It intends to provide the team members with what they need from the outset and allows them to create and add other assets and documentation as they go along. Shopify’s Polaris and Atlassian Design System use this type of design system structure.
Advantages:
- The arrangement is simple to create and implement.
- It encourages the design system team to tell the system’s basic structure from commencement.
- And decisions are made on the move, fast-tracking development.
Drawbacks:
- This arrangement lacks the structure provided by a strict hierarchy.
- Teams tend to list the design system elements alphabetically or by their degree of importance, ignoring critical distinctions.
- And it can be challenging to update and maintain this arrangement.
Atomic design
The atomic design structure was created by design systems advocate and author Brad Frost. It focuses on using order and a structured hierarchy to create an effective UI design system.
The atomic design methodology approaches design system structure by separating the process into five stages. The first three are modeled around the chemistry world, with the subsequent two relating to aspects of the world we can see. We explored atomic design system and its components in a separate article, but let’s recap the most important information here.
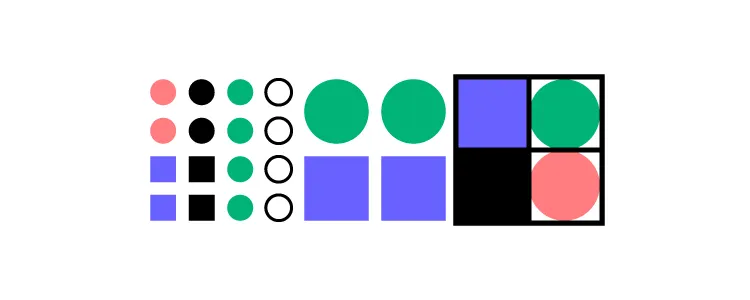
Each stage uses the previous one as its foundation. Every level consists of aggregated items from the preceding one. Like atoms constitute a molecule and molecules form an organism, this structure considers the smallest elemental components before moving on to the larger ones.
- Atoms – These represent the most basic components of the design system.
- Molecules – When those ‘atomic-level’ individual elements combine into groups, you’ll start to see bigger elements, coming together like lego pieces.
- Organisms – By developing combinations of elemental design components into molecular groupings, organisms emerge. These form more complex design system UI components.
- Templates – The next stage departs the realm of chemistry and heads into a more ‘macro’ world. Templates are where organisms can be curated and compiled into a cohesive, recognizable design.
- Pages – Once you take a template and customize it, you have a page. By replacing the placeholder content in templates with tailored design content, you obtain the final, tangible product of the design system. Pages may not need to be designed for each and every case, but ensuring that there exist a few variations is a good idea.
Advantages:
- Atomic design structure makes use of reusable components. Teams can divide various elements into basic atoms. These can then be applied and reapplied in different combinations and configurations.
- Teams can easily spot those parts of a website or app that need various elemental components and create molecules and organisms accordingly.
- This arrangement enables designers to use a design language that clearly defines a separation between content and structure.
- This helps them be more creative and come up with different variants of the same components.
Disadvantages:
- An atomic design structure can result in long, complex lists of components.
- In some instances, having only a few components means maintaining multiple categories for them is pointless. This can complicate the overall methodology.
Code-based design system structure
This approach is among the most potent and effective for designing system structures. It is ideally suited for design teams working on digital product and new functionalities. Think about Material Design or Fluent UI design system.
This structure enables you to develop prototypes that look and behave just like the developer-built final product. This arrangement allows for more collaboration between designers and developers. The whole product team can count on a single source of truth informing their efforts.
The code-based design system arrangement is considered a relatively new approach in digital product system design. With it, designers can now employ functioning, developer-approved coded UI elements to scale digital product design.
Advantages:
- The structure improves designer-developer cooperation.
- It helps teams track changes in UI elements more effectively.
- It improves overall efficiency from prototyping through to design handoff.
Disadvantages:
- Designers need tools like UXPin with Merge tech to benefit from code-based design system.
- Components can take lots of time to create.
- Designers may require developer assistance to develop the system.
How Do You Choose the Right Design System Structure?
Deciding on the right design system structure is essential to giving your team the framework they need to design more efficiently. A design system structure aligned with your product design objectives will help designers collaborate better. This assists them in producing the digital products they’re capable of.
To ensure you’re picking a design system structure that aligns with your product team’s needs, ask yourself:
- For whom is your design system being optimized? Is it for everybody across the organization, user experience designers, or, say, front-end developers only?
- How many components and content types – from design patterns, coded UI components, and design guidelines to rollout plans and best practice policies – are you looking to integrate into the system?
- At what stage of maturity is your design system currently at?
Effective design systems are dynamic entities capable of adapting to the challenges that come with growth and change. A design system’s inherent value lies in its ability to reduce the duplication of effort and facilitated collaboration.
Why UXPin Prefers a Code-Based Design System structure?
Using coded components in a design system enables sharing among design and developer teams. This allows them to rely on a single source of truth and to collaborate more effectively.
Teams across the organization can also manage all their design and prototyping projects simultaneously. This maintains a higher degree of consistency. In turn, developers can get stuck into translating design patterns into developer’s language.
UXPin Merge uses a code-based design system structure to design prototypes with a single source of truth. With it, designers can create prototypes for digital products that are consistent with developer’s workflow. Discover UXPin’s code-to-design solution.